简体中文
繁體中文
English
Pусский
日本語
ภาษาไทย
Tiếng Việt
Bahasa Indonesia
Español
हिन्दी
Filippiiniläinen
Français
Deutsch
Português
Türkçe
한국어
العربية
Starting Forex Trading: What is Leverage and Margin?
摘要:Leverage can greatly amplify profits and losses as merchants can control larger positions using less money (margin). Leverage transactions are also called margin transactions.
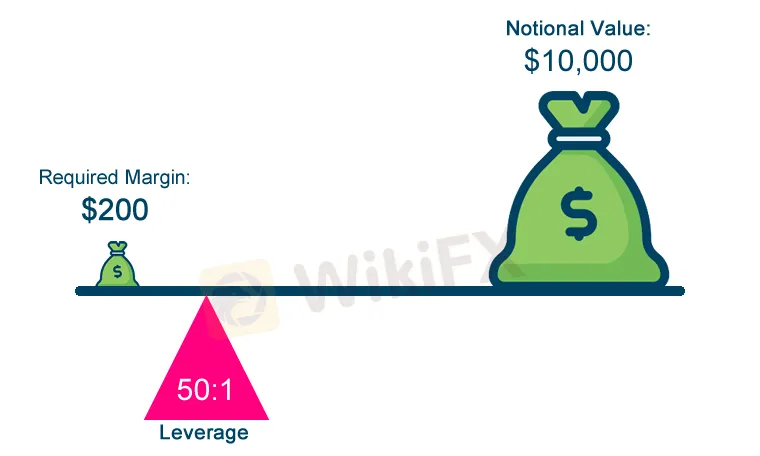
Leverage will amplify potential gains and losses. For example, if you purchase EUR/USD at 1.0000 without leverage, the price will be zero or you will have to double your investment by moving to 2.0000 to bear the total loss. When trading using a total of 100:1 leverage, 100 times less price fluctuations result in the same profit or loss.
Margin is the capital that traders have to raise to open a new position. It is not a fee or cost, and it will be canceled again when the transaction is terminated. The purpose is to protect brokers from losses. If the traders margin falls below a predefined stop-out percentage due to loss, one or all open positions are automatically closed by the broker. The margin call warning from the broker is a warning message that additional deposits are needed in the transaction account to prevent the shortage of evidence needed to maintain the open position.
How leverage and margin works.
With 100:1 leverage, merchants can open positions 100 times larger than they can without leverage. For example, if the purchase cost of EUR/USDs 0.01 litres is generally $1000 and the broker offers 100:1 leverage, the trader must raise it to $100,000. Of course, merchants can use as little leverage as they want.
Caution: The higher the leverage, the higher the risk. Most experts use very low leverage ratios or do not use them at all and use the appropriate risk ratio per transaction.
For more information on leverage, please read the article on what leverage is and how to use it in Forex.
Use a convenient foreign exchange margin calculator to calculate margin requirements based on transaction size and leverage.

免責聲明:
本文觀點僅代表作者個人觀點,不構成本平台的投資建議,本平台不對文章信息準確性、完整性和及時性作出任何保證,亦不對因使用或信賴文章信息引發的任何損失承擔責任
天眼交易商
熱點資訊
因應川普關稅震撼市場,IG取消「保證停損單」手續費
老牌券商Trade Nation值得信賴嗎?監管情形、交易環境、用戶評價、潛在風險一次看
SkyLine Guide 2025 Thailand正式啟動:評審團組建中
WB富格林疑似收割投資人?遭控點差暴利、強制平倉、出金卡關,話術不斷問題多
4/7-4/13最新外匯詐騙券商黑名單公布
外匯市場有哪些值得關注的指標?
SEC Markets疑似無牌經營!高額贈金恐為非法吸金陷阱
匯率計算


